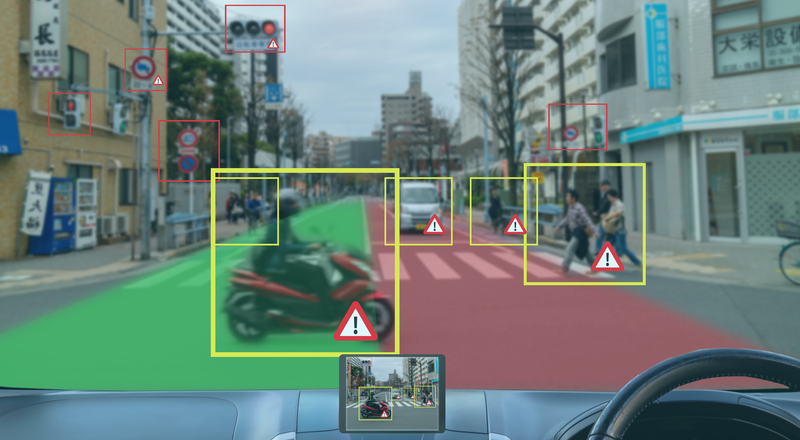
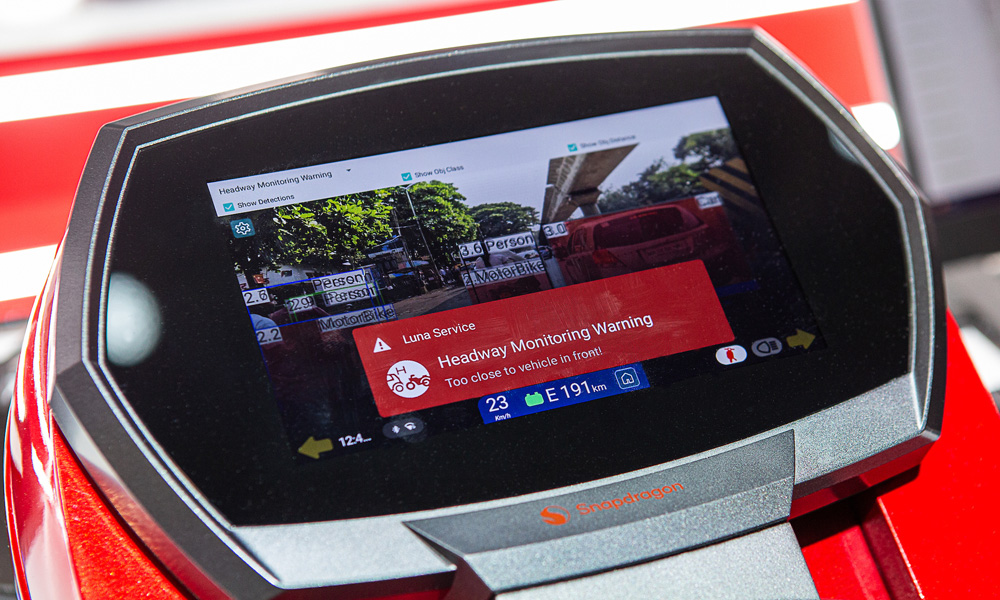
By leveraging advanced communications technologies, connected driving offers the potential to revolutionise transportation systems and significantly alleviate the environmental burdens associated with traditional modes of travel.
This article explores some of the environmental benefits of connected driving, backed by new research from The University of Kaiserslautern-Landau (RTPU), commissioned by Qualcomm Europe, Inc.
From reducing greenhouse gas emissions to optimising trip and mode choice in addition to traffic flow, connected mobility solutions have the potential to reshape the transportation landscape and foster a more harmonious relationship between mobility and the environment.
Driving towards the green zone
In the mobility space, connectivity enables an intelligent vehicle environment that seamlessly integrates state-of-the-art vehicular technology solutions, allowing a heightened communication, cooperation, and interaction on roads. Connected vehicles not only exchange vital information amongst themselves but also establish connections with infrastructure, and other road users, creating new benefits and opportunities for the broader transportation ecosystem.
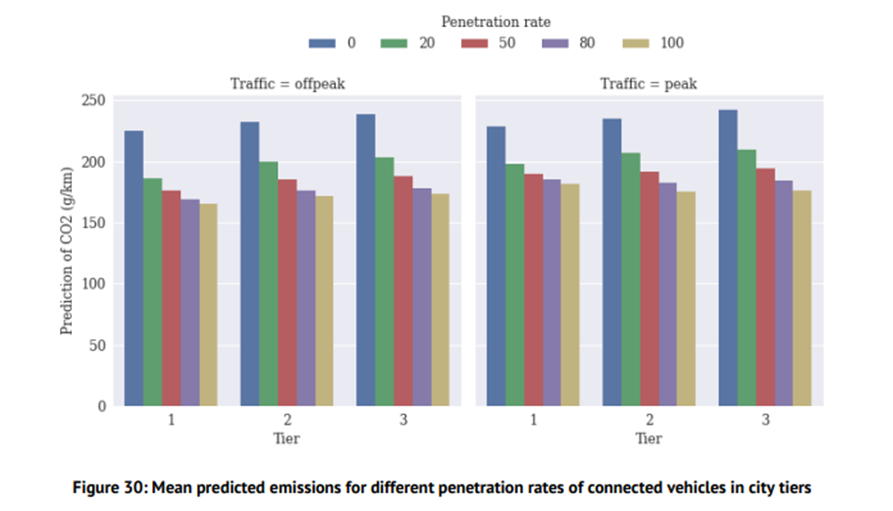
Earlier this year, Qualcomm Europe, Inc. and RTPU shared compelling new research, commissioned by Qualcomm Europe, Inc., that sheds light on the potential of connected mobility to make a significant impact in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing sustainability across the transportation landscape. The study’s findings show that introducing just 20% of connected vehicles on European city roads can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 18%. Some countries, for example Germany, even show potential emissions savings of up to 24%.
This was tested by simulating different traffic scenarios across EU27 cities with populations ranging from fewer than 100,000 to greater than 500,000. The simulation ran during peak-hours (6-9am) and off-peak-hours (12-3pm), testing different penetration rates of connected vehicles ranging from 20% to 80%.
These insights underscore the transformative role that connected vehicles can play in making progress towards a more sustainable future, particularly in Europe. The emissions reduction potential demonstrated by the study would represent significant progress towards achieving the ambitious goals set by the EU Commission’s Green Deal, which aims to achieve a 90% reduction in transport-related emissions by 2050.

This study classifies the different city and rural regions of EU27 into three categories:
Tier 1 (Big City) with population greater than 500,000
Tier 2 (Small City) with population between 100,000 and 500,000
Tier 3 (Rural Area) with population lower than 100,000
The immediate impact of the introduction of (as low as) 20% connected vehicles in EU27 cities (approximately):
Tier 1: emissions can be reduced by 13% during peak hours and 18% during off-peak hours
Tier 2: emissions can be reduced by 14% during peak hours and 16% during off-peak hours
Tier 3: emissions can be reduced by 10% during peak hours and 16% during off-peak hours
Time is emissions
Delays and interruptions, whether due to congested traffic, prolonged idle times, or extended travel durations, contribute to increased emissions. Addressing such inefficiencies through connected driving solutions can help minimise delays, optimise traffic flow and reduce emissions.
The study conducted by RTPU highlights the following connected driving applications that effectively address delays and stoppages, leading to a more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation experience:
Dynamic Routing: By providing vehicles with real-time traffic data and alternative route suggestions, dynamic routing enables drivers to avoid congested areas and helps minimise delays. This optimisation reduces idle time and fuel consumption.
Dynamic Traffic Signals: Dynamic traffic signals adapt their timing based on real-time traffic conditions. By synchronising signals to ensure smoother traffic flow, unnecessary stops and starts are minimised, reducing idle time.
Smart Traffic Junction: By fostering collaboration between connected vehicles and traffic infrastructure, smart traffic junctions aim to improve traffic throughput at intersections. For example, allowing a joint group-start of vehicles at a junction during the green phase of the traffic signal reduces wait times and improves traffic flow, delays and idling.
Junction Optimisation: A combination of dynamic traffic signals and smart traffic junctions, junction optimization helps to efficiently coordinate the movement of vehicles at junctions to safely minimize delays and congestion while enhancing overall traffic flow.
“This study shows that already a limited number of connected mobility applications allow to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and travel times. Furthermore, the applications not only focus on improving traffic efficiency, but also on driver comfort and safety. Thus, connected mobility based on connected and automated driving can contribute to achieve the proposed EU climate action goals in the transportation and mobility sector. This transformation of the mobility landscape will enable societal and economic benefits.”
Are we nearly there yet?
Qualcomm Technologies Inc.’s suite of solutions for the transportation industry are already helping the biggest names in the industry to develop connected vehicles and increase their numbers on the road. To date, Qualcomm Technologies has announced collaborations with Renault, Mercedes, Stellantis, BMW, VW/Cariad, and Volvo, to create a new generation of software defined vehicles that are highly connected to their surroundings and each other.
The Snapdragon® Digital Chassis™ Solution by Qualcomm Technologies comprises a set of cloud-connected automotive platforms for telematics and connectivity, cockpit, and driver assistance and autonomy. These platforms enable vehicles to gather and process massive amounts of data that can be uploaded to cloud platforms for more personalised in-vehicle experiences, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and enhanced automated driving capabilities. This enables a connected vehicle ecosystem that allows for seamless interactions between vehicles, infrastructure, and vulnerable road users, leading to safer driving experiences, improved traffic efficiency and lower emissions.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities continue to evolve, the interconnectivity between vehicles and their surrounding environment holds promising opportunities to enhance sustainability even beyond the automotive industry.
From an enterprise level, Qualcomm Technologies is also helping businesses reduce the environmental impact of supply chains. Currently, the supply chain often accounts for over 90% of an organisation’s greenhouse gas emissions. Qualcomm Technologies’ recently announced Qualcomm Aware™ Platform leverages the power of cloud-connected intelligence to create real-time asset visibility, location, and condition monitoring solutions across industries, including the supply chain.
This will give organisations a holistic view of their supply chains, allowing them to take decisive action during transportation routes, making them as efficient as possible, thus minimising emissions. As a longer team goal, the Qualcomm Aware platform will also help enterprises overcome the current fragmentation in the IoT space, to help ensure everyone and everything can be connected. This is a critical step to unlocking the full emission-saving potential of the connected vehicle and smart IoT devices.
Embracing the emission-savings potential of a connected environment, both within the automotive sector and beyond, will be instrumental in paving the way towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly world. By harnessing the power of connectivity, we can drive meaningful change and contribute to a greener future for generations to come.
Content produced in association with Qualcomm
Snapdragon and Qualcomm branded products are products of Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries