Geoff Hadwick reports on TISPOL’s efforts to protect vulnerable road users.
At its annual conference in Manchester,
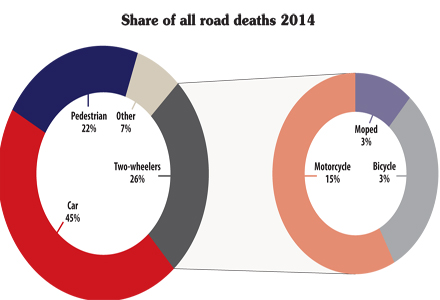
In regards to motorcycle and bicycle casualties, TISPOL highlights a recent AA Populuspoll of 17,629 drivers in the UK. There results were clear: “Failure to look properly is the most commonly cited (44%) contributory factor in UK road crashes where in 2014 the number of fatalities among motorcycle and bicycle riders increased to 339 (from 331 in 2013) and to 113 (from 109 in 2013) respectively.” Despite the fact that motorbikes make up just 1% of traffic, motorcyclists account for 19% of all road fatalities. “They are 55 times more likely than car drivers to be killed or seriously hurt in an accident,” said the AA report.
Why? Because “nine out of ten drivers (93%) admit it is sometimes hard to see cyclists while driving” said the survey. “85% say it is hard to see motorcyclists and more than half (55%) are often ‘surprised when a cyclist appears from nowhere’.”
One possible factor in this increase, and the levelling out of falls in road deaths across the EU, is the increasing age demographic profile both in Europe and indeed in other areas of the world too.
“Are there too many drivers who are just too old to be on the road, Sergeant Rob Heard of Hampshire Police asked?
If the average driver’s reaction times, eyesight, spatial awareness and hearing are all impaired by age, is there a case for targeting this part of the road user community more effectively? Heard talked the conference through an “Older drivers’ forum” project in which he has been working.
The scheme sets up an “awareness week” and visits six different local venues. More than “100 older drivers attended on each day,” Heard said. “We gave advice on: brushing up their driving skills; booking a voluntary driving assessment; having a free eyesight test and arranging a regular eyesight tests; getting advice on health and well-being issues that could affect their driving ability; advice on renewing their licences at 70; learning more about road safety and the consequences of not being fit to drive; and discovering alternatives to driving and staying independent without a car.”
Fatigue came up several times during the conference. Yvonne Taylor of North Yorkshire Police spoke about the effects shift working has on driving habits – a subject she is studying as part of a PhD she is doing with Leeds University’s Institute for Transport Studies. As an indication of its significance, she said there are 3.5 million shift workers in the UK and cited a raft of recent research papers which show that that sleepiness peaks are generally between 3am and 5am and again between 2pm and 4pm. These times correlate with increases in fatigue-related road traffic collisions and she said shift work-induced fatigue is a significant risk factor increasing the likelihood of accident and injury. Figures show that fatigue accounts for up to 20% of serious collisions on motorways and monotonous roads in Great Britain and that police shift work is associated with a high prevalence of sleep disorders and self-reported drowsy driving.
Having surveyed colleagues who work on a rotating shift pattern, and concluded that there is no such thing as a morning or an evening person … everyone is vulnerable to a lack of regular sleep. Taylor’s initial findings show that “in the 12 months preceding the study, 5.8% [of participants] said they had been involved in a collision or road departure on the way to or from work. More than half, 51.9%, stated that they had been involved in a ‘near miss’ such as a kerb strike, lane departure or near-collision.”
Almost all of these incidents (95.7%) happened on the way home from work and 61.8% of those involved had been working a nightshift prior to the incident.











